Storing metadata against Azure Storage Blobs
I've known for a while that you can associate aribitrary metadata with Azure Storage Blobs, docs.microsoft.com has Set and retrieve properties and metadata which gives an example of setting metadata on a container (which I didn't know you could do!) and there's also various questions on Stack Overflow. It does seem like it's the slightly forgotten relative, a little bit like Alternate Data Streams (ADS) for NTFS filesystems - though that's where the analogy stops and starts; beyond that they're not that similar at all!
So, what is Blob metadata and how do I use it?
The linked documentation breaks metadata down into two forms, System properties and User-defined metadata. I'm going to look exclusively at the latter, which is defined in that documentation as:
User-defined metadata is metadata that you specify on a given resource in the form of a name-value pair. You can use metadata to store additional values with a storage resource. These additional metadata values are for your own purposes only, and do not affect how the resource behaves.
So the definition of metadata for Azure Blobs, when you distill it, isn't really different to the general definition of metadata, as seen here from dictionary.com:
information that is held as a description of stored data
Nothing too exciting, or special, about it. But it does mean that you've got somewhere that you can store associated metadata for files that you've stored into Azure blobs. Unlike with ADS on NTFS with the "in the left-hand Explorer window I have an NTFS filesystem with files that have ADS associated with them and in the right-hand Explorer window I have a FAT32 filesystem, ready and waiting to dispose of the ADS data as I copy files across" scenario, using Azure Storage blobs is (a) sufficiently new, and (b) sufficiently different that this should hopefully not be a problem. In other words, it's worth using.
You could, rather than storing information in metadata, spin up an associated Table Storage table to store the metadata in. In some situations that might be absolutely the right thing to do, but if there's just a few pieces of data to be stored then storing them directly against the Blob is one way to go. Lets use an example wher we're uploading images from a scanner (for archival purposes) to Blob storage. They're probably never going to be looked at again, but if one is, the bits of metadata may come in handy - perhaps it's details of where the physical box that holds the scanned document is stored.
Creating a Blob and adding metadata values to it
I'm using the code from my recent Using the Azure Storage Emulator post as it gives a simple code sample for creating a blob, that doesn't rely on anything other than the Storage Emulator being available, so if you've somehow got to this post when on a plane, but can't get ot Azure - you're in luck! It also does a typically developer-ish thing and creates a new container, named with a GUID to avoid collisions, then creates the blob, again named with a GUID just to be extra-special-certain. If you want to be able to see what's happening when you drop into Storage Explorer more easily, change these. There's no reason other than being extra-special-certain to avoid collisions that this code is littered with GUIDs. So, the code:
using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage;
using System;
namespace ConnectoToStorageEmulator
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var containerName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
var blobName = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
var cloudStorageAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(@"UseDevelopmentStorage=true");
var blobclient = cloudStorageAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
var container = blobclient.GetContainerReference(containerName);
container.Create();
var blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(blobName);
blob.UploadText("1234");
// Add metadata to blob
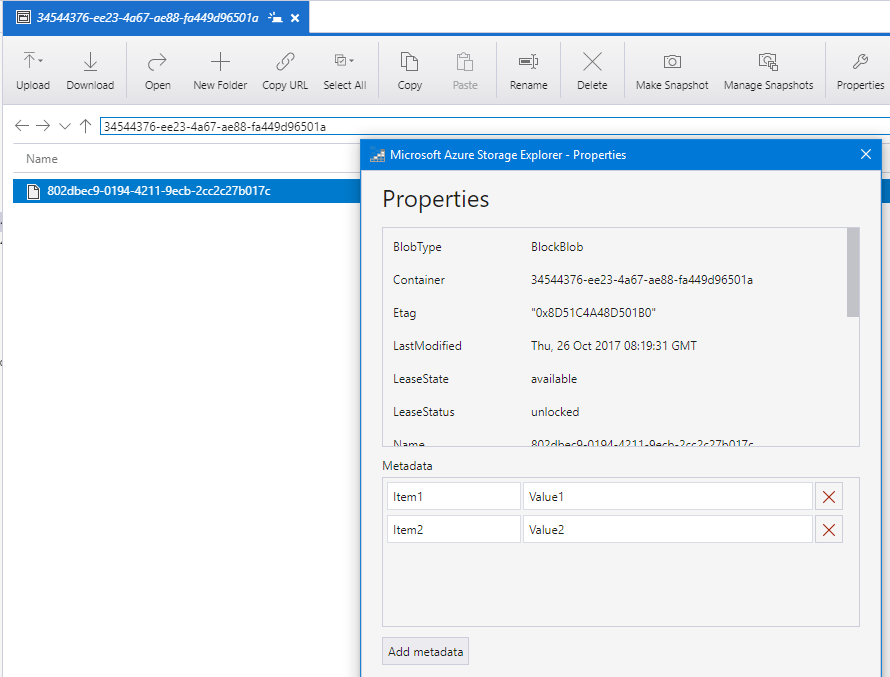
blob.Metadata["Item1"] = "Value1";
blob.Metadata["Item2"] = "Value2";
blob.SetMetadata();
}
}
}
If you compare the code above to the code in the Storage Emulator post, you'll see that the only change I've made is the addition of the three lines (four if you include the comment) at the bottom of the Main method, two to set some Key/Value Pairs and one to persist them back to Azure Storage. That's it, that really is all there is to it. To see the metadata in situ, you can drop into the Azure Storage Explorer, drill-down to the blob in question and look at its properties.
You can also access the metadata programatically:
var blobReloaded = container.GetBlockBlobReference(blobName); blobReloaded.FetchAttributes(); Console.WriteLine(blobReloaded.Metadata["Item1"]); Console.WriteLine(blobReloaded.Metadata["Item2"]);
The code above is intended to slot into the previous example, immediately after the code to save the call to .SetMetadata(). This example of programatically inspecting the metadata for a blob shows something important, if you don't call FetchAttributes then the metadata for your blob won't be loaded and will show as being empty. This is something that seems to catch people out, as there was more than one "why isn't my metadata being saved?" question out there that was answered with "it is, you're just not loading it!".